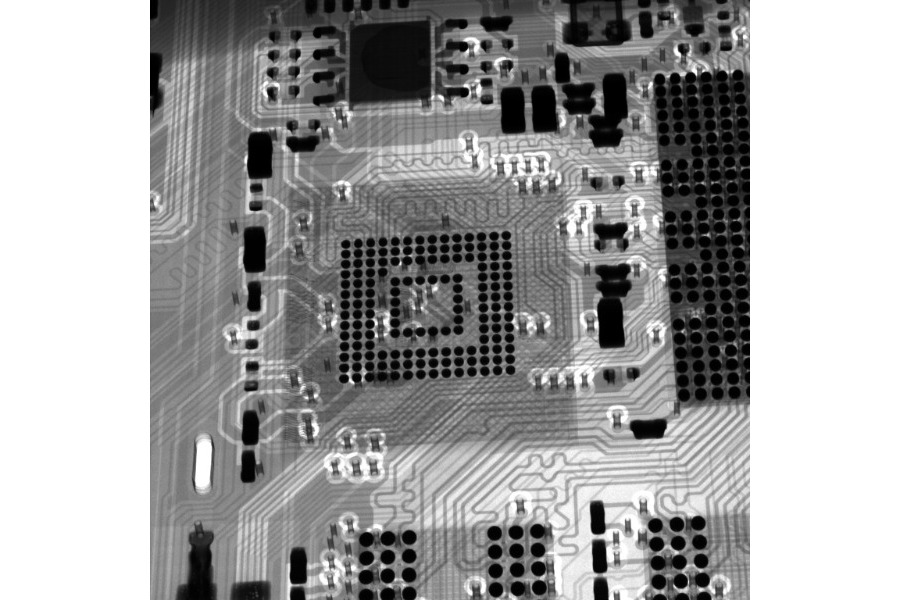
Skip to contentCPU Packaging Technology Comparison: BGA and LGA
wellman2023-11-08T10:19:05+08:00In the world of computer hardware, central processing units (CPUs) play a crucial role in the performance and functionality of a computer system. When it comes to CPU packaging, two popular technologies stand out: Ball Grid Array (BGA) and Land Grid Array (LGA). In this article, we will delve into the details of these two packaging technologies, comparing their features, advantages, and disadvantages.

Ball Grid Array (BGA):
BGA is a packaging technology commonly used in CPUs and other integrated circuits. In BGA, the CPU chip is mounted on a small substrate, and tiny solder balls are attached to the underside of the chip. These solder balls act as the connection points between the chip and the motherboard.
Advantages of BGA:
a) Thermal Performance: BGA offers excellent thermal performance due to its large number of solder balls. This allows for efficient heat dissipation, which is crucial for high-performance CPUs.
b) Compact Size: BGA packages are smaller in size compared to other packaging technologies. This makes them ideal for devices with limited space, such as laptops and mobile devices.
c) High Pin Density: BGA packages can accommodate a high number of pins, allowing for increased connectivity and functionality.
Disadvantages of BGA:
a) Non-Upgradeable: BGA CPUs are soldered directly onto the motherboard, making them non-upgradeable. If a BGA CPU fails or needs an upgrade, the entire motherboard may need to be replaced.
b) Difficult Repair: BGA packages are challenging to repair due to the soldered connections. Specialized equipment and expertise are required to rework or replace a BGA CPU.
Land Grid Array (LGA):
LGA is another popular packaging technology used in CPUs. In LGA, the CPU chip is mounted on a substrate, and an array of pins is attached to the underside of the chip. These pins make direct contact with the motherboard’s socket, providing the necessary electrical connections.
Advantages of LGA:
a) Upgradeability: LGA CPUs can be easily upgraded or replaced without replacing the entire motherboard. This flexibility allows users to keep up with the latest CPU advancements without significant hardware changes.
b) Easy Repair: LGA packages are relatively easier to repair compared to BGA. If a CPU fails, it can be replaced by simply removing it from the socket and installing a new one.
c) Better Electrical Performance: LGA offers improved electrical performance due to the direct contact between the CPU pins and the motherboard socket. This results in lower resistance and better signal integrity.
Disadvantages of LGA:
a) Larger Size: LGA packages are generally larger in size compared to BGA. This can be a limitation in devices with space constraints.
b) Lower Pin Density: LGA packages typically have a lower pin density compared to BGA. This may limit the connectivity options and functionality of the CPU.
Conclusion:
Both BGA and LGA are widely used CPU packaging technologies, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. BGA offers excellent thermal performance and compact size but lacks upgradeability and repairability. On the other hand, LGA provides upgradeability, easy repair, and better electrical performance, but at the cost of larger size and lower pin density.
When choosing between BGA and LGA, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the computer system and the intended usage. Whether it’s a high-performance gaming rig or a compact laptop, understanding the differences between these packaging technologies will help in making an informed decision.
In conclusion, CPU packaging technology plays a crucial role in the overall performance and functionality of a computer system. By comparing BGA and LGA, users can make an informed decision based on their specific needs and requirements.
Share this to your social media